Phishing



How an MSP Strengthens Your Business’s Cybersecurity Posture

Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. With threats like ransomware, phishing, and data breaches on the rise, businesses must take a proactive approach to security. But should you handle cybersecurity in-house or partner with a Managed Service Provider (MSP)?
1. Do You Have the Budget for an In-House Cybersecurity Team?
Hiring and maintaining an in-house cybersecurity team requires significant investment in salaries, training, and cutting-edge security tools. MSPs provide enterprise-grade security at a predictable cost, making cybersecurity more affordable without sacrificing quality.
2. Can Your Business Handle 24/7 Threat Monitoring?
Cyber threats don’t follow business hours. If your company lacks the resources for round-the-clock monitoring and rapid incident response, an MSP ensures constant protection, identifying and stopping threats before they escalate.
3. Are You Prepared for Compliance & Regulatory Requirements?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce must follow strict cybersecurity regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS). MSPs specialize in compliance management, ensuring your business meets legal requirements and avoids costly fines.
4. Do You Have the Right Security Tools & Expertise?
Cybercriminals continuously evolve their tactics, and keeping up requires advanced security solutions like intrusion detection, endpoint protection, and AI-driven threat analysis. MSPs provide access to top-tier security tools and skilled experts without the overhead of purchasing and managing them yourself.
5. How Fast Can You Recover from a Cyberattack?
A cyberattack can lead to data loss, system downtime, and reputational damage. MSPs offer disaster recovery and backup solutions, ensuring your business can quickly restore operations and minimize losses.

Key Features of an Ideal MSP
- Offer a flexible service model
- Take a shared approach to managed services
- Have a solid strategic relationship with either your solutions or cloud provider
- Have many consultants available
- Offer advanced services
- Utilize remote monitoring and management for proactive maintenance
- Have a solid backup and disaster recovery strategy
- Have an established escalation path and provide a secondary contact
- Work with your legal team to address compliance issues
The Bottom Line
If your business lacks the budget, expertise, or resources for comprehensive cybersecurity, partnering with an MSP is the smart choice. By outsourcing cybersecurity to professionals, you get 24/7 protection, cost savings, compliance support, and peace of mind, allowing you to focus on growing your business. As cyber threats continue to rise, investing in an MSP is a strategic move that enhances your cybersecurity posture, compliance, and peace of mind.
🚀 Stay Secure. Stay Ahead. Consider an MSP Today! 🚀
Ready to enhance your cybersecurity posture?
🔹Contact Applied Technology today and take the first step towards a more secure future! 🔹

MSP’s to Enhance Business Efficiencies
A Managed Service Provider is a company that offers a range of IT services to businesses on an ongoing basis.
Instead of handling IT tasks in-house, companies outsource their IT needs to an MSP who will proactively manage and support their systems, networks, and technologies. MSPs typically offer services like network management, cybersecurity, data backups, cloud services, helpdesk support, and system monitoring.
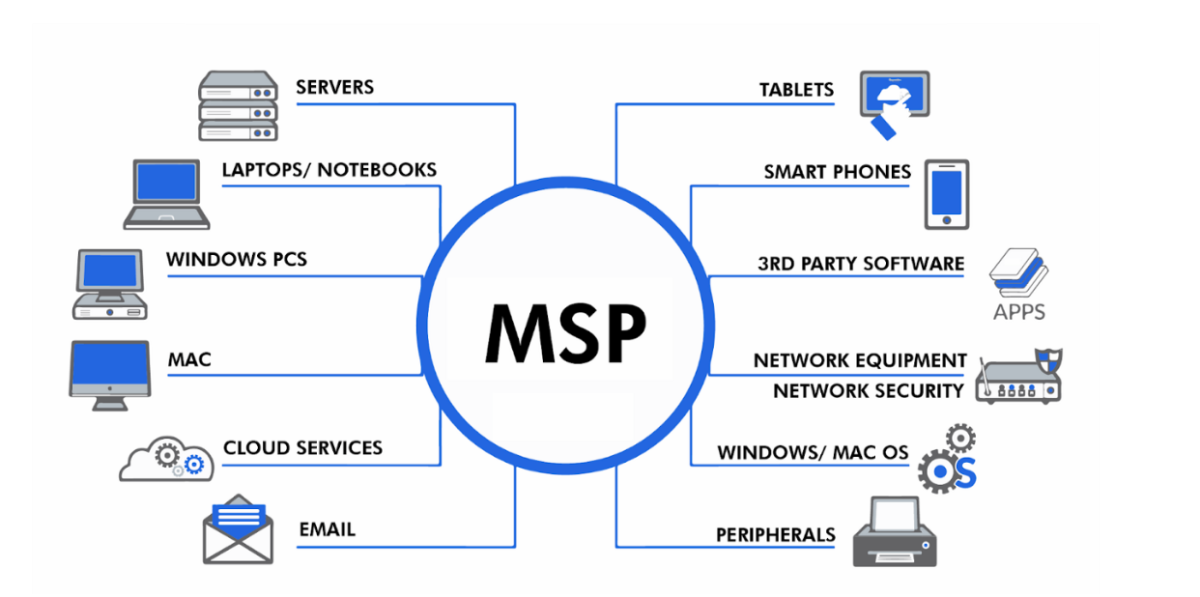
Here’s how an MSP can enhance your business:
- Cost Savings: MSPs provide affordable IT services with a predictable monthly fee, avoiding the need for an in-house team.
- Expertise: Access to specialized knowledge and advanced tools without hiring or training staff.
- Proactive Monitoring: Continuous system monitoring to prevent downtime and resolve issues before they escalate.
- Scalability: Services can easily grow with your business, adapting to new needs.
- Cybersecurity: Robust protection against cyber threats, ensuring data security.
- Focus on Core Business: Free up internal resources to focus on strategic goals instead of tech issues.
- Disaster Recovery: Backup systems and recovery plans to minimize data loss and downtime.
How Using an MSP Works for Your Business:
When you partner with an MSP, they first assess your current IT setup and identify areas for improvement. They’ll then implement tailored solutions to fit your specific business needs. Ongoing support and maintenance are part of the package, so you don’t have to worry about tech issues disrupting your operations. With a dedicated team managing your IT, your business can run more efficiently, securely, and without the stress of dealing with tech problems. The MSP acts as an extension of your business, providing continuous support to help your company grow and evolve.
Overall Statement:
By leveraging the expertise of an MSP, businesses can offload their IT management, ensuring systems are secure, up-to-date, and running smoothly. This allows them to focus on growth and innovation, rather than getting bogged down by technical challenges, leading to increased productivity, reduced risks, and long-term success.
Ready to take your business to the next level?
Let us handle the tech while you focus on what you do best. Reach out to us today at sales@atgfw.com or call 260-482-2844.
We’re here to help you grow!

Implementing MFA: A Layered Approach to Securing Data
What Is MFA and How Is It Different from 2FA?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process requiring two or more verification factors to gain access to a system. It’s an enhancement of two-factor authentication (2FA), which typically combines two elements (e.g., password + a one-time code). MFA goes further, allowing for three or more factors, such as biometric data or behavioral analysis, for an additional layer of security.
Why Implement MFA?
MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access by adding layers of verification beyond passwords, which are vulnerable to phishing and breaches. Businesses use MFA to protect sensitive applications, data, and systems, especially for remote or traveling employees who connect from varied locations.
For example, a traveling employee accessing company files from a hotel Wi-Fi network is a prime target for cybercriminals. Without MFA, a stolen password could lead to a full system compromise. With MFA, even if a password is stolen, the attacker would still need a second (or third) factor—like a hardware key or fingerprint—to gain access.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA:
- Select Reliable MFA Methods:
Use secure options like:- Hardware security keys (e.g., YubiKeys)
- Biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition)
- Push notifications through secure apps (e.g., Microsoft Authenticator or Duo).
- Avoid Weak MFA Methods:
Avoid SMS-based authentication, as text messages can be intercepted through SIM-swapping or phishing attacks. - Ensure Compatibility:
Choose solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing tools and workflows. - Educate Employees:
Train your staff on the importance of MFA and how to use it effectively.
MFA is a critical investment to protect your business in today’s evolving cybersecurity landscape. Ensure your data stays safe by implementing robust, layered defenses.
PRO TIP
Check to see whether your email accounts, banks, healthcare providers, and other important accounts offer MFA and enable it by default. If they don’t, ask them why not. It’s your information they’re putting at risk!
Take Action Today!
Your company’s security is more than a simple password. Implementing MFA is a vital step toward safeguarding your business. Let Applied Technology Group help you create a secure, layered defense strategy tailored to your needs. Contact us today at Sales@atgfw.com or 260.482.2844 to get started.
“Passwords vs. AI Hackers: Your First Line of Defense in 2025”
In a world where AI hackers never sleep, your best weapon is preparation.
In 2025, advanced AI hackers are pushing cybersecurity to the brink. A strong password is your first line of defense in this digital arms race. Protecting your data starts with mastering the basics: strong passwords. Here’s why they matter and how to stay ahead:
- AI Hackers Are Smarter Than Ever: Machine learning enables them to guess weak passwords in seconds, exploiting simple combinations like “123456” or “password.”
- What Makes a Password Strong:
- At least 12 characters long.
- A mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Unique for every account—no repeats!
- Leverage Tools for Extra Security:
- Use password managers to generate and store complex passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to create an additional security layer.
- Avoid Common Mistakes:
- Don’t use personal info (birthdates, pet names, etc.).
- Steer clear of dictionary words or predictable patterns like “abc123.”
Don’t let AI hackers catch you off guard, because when it comes to cybersecurity, it’s better to be paranoid than sorry!
Partner with Applied Technology Group for robust cybersecurity solutions that safeguard your data, accounts, and peace of mind. From password management to comprehensive security strategies, we’ve got you covered.
📞 Contact us now to learn how we can help protect your organization against evolving threats 260.482.2844 | Sales@atgfw.com.
Let’s secure your future together!

Fixing Your Weakest Link: Your Employees
Phishing: Part 3
You can have every piece of security hardware in the books: firewall, backup disaster recovery device, and even anti-virus. However, your employees will still be the biggest vulnerability in your organization when it comes to phishing attacks. How do you mitigate as much risk as possible?
- Create and Strictly Enforce a Password Policy: Passwords should be complex, randomly generated, and replaced regularly. In order to test the strength of your password go to howsecureismypassword.com. (This is a perfectly safe service sponsored by a password protection platform that tells you how long it would take a hacker to decode your password.) When creating a password policy, bear in mind that the most prevalent attacks are Dictionary attacks. Most people utilize real words for their passwords. Hackers will typically try all words before trying a brute force attack. Instead of words, use a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. The longer the password, the stronger it is. While it’s difficult to remember passwords across different platforms, try not to repeat passwords. This will protect all other accounts in the event of a breach on one of your accounts.
- Train and Test Your Employees Regularly: Educate your employees on how they can spot a phishing attack. Then, utilize penetration testing (this is a safe phishing attack orchestrated by your IT company to see how employees respond) and how well they do. If employees fall for phishing attempts then send them through training again. We recommend doing this on a quarterly basis to ensure that your employees stay on their toes and you should provide education on the latest attacks.
- Create a Bring Your Own Device Policy and Protect all Mobile Phones: You can safeguard as much as humanly possible on your network, but your employees are all walking in with cell phones. Are they allowed to get work emails on their phones? What about gaining access to the network remotely? Cell phones create a big black hole in security without proper mobile device management and mobile security.
- Perform Software Updates Regularly: Make sure that your software is up-to-date with all the latest security patches. Holding off on updates means that you’re leaving yourself open to vulnerabilities that have been discovered and addressed.
- Invest in Security: Security is not something for cost savings. Home-based hardware is not sufficient, and you, at the very least need a quality firewall and backup device. Invest in your employee’s training, ongoing security updates, and maintaining a full crisis/breach plan.
There are two things that aren’t going away in any business, employees and security threats. Make sure that you’ve taken care of everything you can to avoid falling victim to these attacks.

How to Spot A Phishing Attack
Phishing: Part 2
Would you know if you were the subject of a phishing attack? Many people claim that they’d be able to tell right away if they received an email from an illegitimate source. If that were the case, there wouldn’t be 1.5 million new phishing websites every month. A 65% increase in attacks in one year! Hackers would have moved on to their next idea for swindling people out of their identities and money. How do you spot a phishing attack and avoid falling victim yourself?
Look for these red flags:
Sender Email Address: Always check to make sure that the email address is legitimate. Amateur hackers will send things from Gmail or Hotmail accounts and hope you don’t notice. More sophisticated hackers will closely mimic an actual email domain, like amazonprime.com rather than amazon.com. Double check the email address before responding, clicking, or opening, even if the from name appears correct.
Discrepancies in Writing Format: If the attack is coming from overseas, you’re likely to notice some small issues in writing format, like writing a date as 4th April, 2019 rather than April 4, 2019. While this is subtle, it should be a red flag.
Grammar Issues: We all fall victim to the occasional typo, but if you receive an email riddled with grammar and spelling mistakes, consider the source. It’s likely from a hacker, especially if the email supposedly comes from a major organization.
Sender Name: This one is also difficult to track, but phishing emails will typically close with a very generic name to avoid raising suspicion. You should recognize the people that send you emails, or at the very least clearly understand their role at the organization.
Link Destination: Before you click on any link in an email be sure to hover over it. The destination URL should pop up. Check out the domain name of this URL. Similar to the sender email address, make sure that this address is legitimate before clicking.
Attachments: Is it realistic to expect an attachment from this sender? Rule of thumb, don’t open any attachment you don’t expect to receive, whether it’s a Zip file, PDF or otherwise. The payload for a ransomware attack often hides inside.
Email Design: A kooky font like Comic Sans should immediately raise red flags, especially if you don’t clearly recognize the sender.
Links to Verify Information: Never ever click on a link to verify information. Instead, if you think the information does need updating go directly to the website. Type in your email and password, and update your information from the Account tab. Always go directly to the source.
Odd Logo Use: Hackers try their best to mimic a websites’ look and feel. Oftentimes, they get very close; but they won’t be perfect. If something feels off, it probably is.
While there is no fool-proof method for avoiding falling victim to a phishing attack, knowing how to spot likely culprits is one step in the right direction. We’ll cover other protective measures to reduce your risk of falling victim to phishing attacks in our next blog.

What Is Phishing & How Are Hackers Using It?
Phishing: Part 1
While the number of people falling for sending personal information to the crown prince of Nigeria in hopes of receiving his promised wealth and riches seems to be dropping, phishing remains a major issue. In fact, the number of phishing campaigns pursued by hackers around the world increased 65% in the last year.
What exactly is phishing? Hackers mimic the emails, forms, and websites of legitimate companies in an effort to lure people into providing their private, personal information, like credit card numbers, social security information, account logins, and personal identifiers. The victim typically doesn’t realize they’ve been compromised until long after the event, and oftentimes only after their identity or finances are affected. In the past, an attack was carried out relatively quickly. As soon as the victim gave up their information, the hacker moved in and stole money from the compromised account. Today, it’s often more lucrative for hackers to sell that information on the Dark Web, resulting in longer-lasting and even more devastating attacks.
3 Types of Phishing Attacks
Spear Phishing
Phishing attempts directed at specific individuals or companies have been termed spear phishing. Attackers may gather personal information about their target to increase their probability of success. This technique is by far the most successful on the Internet today, accounting for 91% of attacks.
Threat Group-4127 used spear phishing tactics to target email accounts linked to Hillary Clinton‘s 2016 presidential campaign. They attacked more than 1,800 Google accounts and implemented accounts-google.com domain to threaten targeted users.
Clone Phishing
Clone phishing is a type of phishing attack whereby a legitimate and previously delivered email containing an attachment or link, has had its content and recipient address(es) taken and used to create an almost identical or cloned email. The attachment or link within the email is replaced with a malicious version and then sent from an email address spoofed to appear as though it came from the original sender. It may claim to be a resend of the original or an updated version to the original. This technique could be used to pivot (indirectly) from a previously infected machine and gain a foothold on another machine, by exploiting the social trust associated with the inferred connection due to both parties receiving the original email.
Whaling
Several phishing attacks have been directed specifically at senior executives and other high-profile targets within businesses. The term whaling has been coined for these kinds of attacks. In the case of whaling, the masquerading web page/email will take a more serious executive-level form. The content will be crafted to target an upper manager and the person’s role in the company. The content of a whaling attack email is often written as a legal subpoena, customer complaint, or executive issue. Whaling scam emails are designed to masquerade as a critical business email, sent from a legitimate business authority. The content is meant to be tailored for upper management, and usually involves some kind of falsified company-wide concern. Whaling phishers have also forged official-looking FBI subpoena emails and claimed that the manager needs to click a link and install special software to view the subpoena.
Have you ever gotten an email from your bank or medical office asking you to update your information online or confirm your username and password? Maybe a suspicious email from your boss asking you to execute a wire transfer. That is most likely a spear phishing attempt, and you’re among the 76% of businesses that were victims of a phishing attack in the last year.
Method of Delivery
Phishing scams are not always received through email and hackers are getting trickier and trickier with their preferred method of execution. In 2017, officials caught onto attacks using SMS texting (smishing), Voice phishing (vishing) or social engineering, a method in which users can be encouraged to click on various kinds of unexpected content for a variety of technical and social reasons.
Ransomware: The Consequence
Phishing is the most widely used method for spreading ransomware, and has increased significantly since the birth of major ransomware viruses like Petya and Wannacry. Anyone can become a victim of phishing or in turn, ransomware attacks. However, hackers have begun targeting organizations that are more likely to pay the ransoms. Small businesses, education, government, and healthcare often, don’t have valid data backups. Therefore they are unable to roll back to a pre-ransomed version of their data. Instead, they have to pay their way out or cease to exist. Outside of ransom costs, victims of phishing campaigns are often branded as untrustworthy and many of their customers turn to their competitors, resulting in even greater financial loss.
Why are effective phishing campaigns so rampant despite public awareness from media coverage?
Volume: There are nearly 5 million new phishing sites created every month, according to Webroot Threat Report. There are now even Phishing as a Service companies, offering phishing attacks in exchange for payment. One Russian website, “Fake Game,” claims over 61,000 subscribers and 680,000 credentials stolen.
They work: Over 30% of phishing messages get opened, and 12% of targets click on the embedded attachments or links, according to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report. In short, these hackers have gotten really good at looking really legitimate.
They’re simple to execute: New phishing campaigns and sites can be built by sophisticated hackers in a matter of minutes. While we think there are far more legitimate ways to be earning money, these individuals have made a living out of duplicating their successful campaigns.
Now that you have an understanding of what phishing is, our next two blogs will teach you How to Spot a Phishing Attack, and Fixing Your Weakest Link: Your Employees.

8 Biggest Threats to Small Businesses
Breaches: Part 2
We still see the same scene in horror movies: the main character runs into the house, slams the door, locks the deadbolt and sighs in relief — but somehow the killer still sneaks up and attacks them from behind!
If you own a small business you just might find yourself in a similar situation. Sometimes small business owners spend large amounts of time and resources physically protecting their operations just to let the most dangerous threats sneak in through the figurative back door.
Today we’re going to talk about the 8 biggest security threats to small business in 2019, in no particular order. While a few of them are new, some past risks are still very much in play.
Phishing
Not only is this the number one threat to cybersecurity, it’s also still on it’s way up. Phishing attempts were reported by 48% of small businesses in 2017 — up from 42% just one year prior. All indications point to this trend rising as it requires the least amount of resources and knowhow to attempt.
Microsoft Document Scams
There’s nothing safer than opening up a Word document, right? Think again! For the past few years, scammers have been getting creative with coding that allows them to gain access to your computer, which is why Microsoft has been having to work overtime to create new patches. However, since many companies delay updating their software, this remains a prime option for criminals.
Ransomware
Currently, over 1,100 different variations of ransomware are being tracked around the world. The FBI has stated that there has been a sharp uptick in these attacks recently and they advise that the practice will continue to grow rapidly the coming years. So far this year, not just businesses, but entire cities have paid ransoms to get their data back.
Cryptojacking
As cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have exploded on the scene, their demand and value have gone up as well. Although you can’t physically mint a Bitcoin as you could a dollar bill, they are “created” in a process known as mining. This is a resource-intensive practice that requires computing power that thieves often lack. The solution? Hijack other computer systems to do the computing for them, taking a toll on bandwidth and slowing down networks.
Internet of Things (IoT) Attacks
Technology is rapidly increasing, not just in computing devices, but in everything that’s become a computing device. With IoT technology, you can connect your servers to your security system, HVAC system — even the microwave in your break room! While this allows everything to be connected and consolidated in one place, it also creates vulnerabilities. Most of these devices have very weak security protocols in place: who would want access to the toaster in the office next door? But as they are often connected to the main network, it creates a backdoor that can — and has repeatedly been — exploited.
Mobile Devices
Many small businesses feel safe doing business on their mobile devices only to have them be one of their weakest points. While most of us have been lectured about using unsecured Wifi ad nauseam, the most recent threat to mobile computing is our reliance on the Cloud. In the past few years, companies such as Apple, Google, and Microsoft have made cloud backups a standard part of their services. Since so much information is stored in one location, it creates a prime target for criminals to attack and gain access to your information. While that may not be a problem if you’re just backing up family photos or text messages from your sister, any important documentation or other data for your business may have also found its way onto these mega servers without you even realizing it.
Undertrained Employees
What has been mentioned to this point is just a sample of the ever-evolving external cyber threats to your business. While an easy fix might be to hire someone who just graduated from a reputable university, the truth is, that may not be enough. A recent study showed that 40% of companies surveyed said that having employees with an applicable degree has shown not to be good enough to keep their systems safe. That same survey showed that less than 25% of applicants for cybersecurity positions were deemed qualified. If that’s how things look in your company, you may feel safe today, but might be in danger for what’s coming over the horizon. It is estimated that training someone to do the job well takes over six months!
Understaffed Security
In line with the last point, an estimated 69% of companies will have an understaffed cyber threat team, with a large portion of this being companies with absolutely no one in this role at all. What does this mean for a small business? Either people with no experience will have to fill this position, or there is nothing in place to protect valuable data from hackers.
The killer hiding in the back seat, sneaking in through the back door, or — even worse — he’s already in the house, are all clichés. Do you know what else is cliché? Letting your small business fall victim to cyber-attacks. While not all attacks might be avoidable, you’re much safer from attacks if you’re prepared. Updated security software and regular data back-ups are invaluable in this process. Awareness of the latest threats is also key. Just like in the movies; when a killer is loose, no one should feel safe.
